The Three Phases to Lifecycle Stage Tracking Optimization

How long does it take for a lead to get to closed won? Out of how many prospects enter the funnel, how many become Marketing Qualified Leads (MQL’s)? How many turn into meetings and then pipeline? What is the velocity from MQL to that first sales meeting? Lifecycle stage tracking reveals the answers to all of these questions and more.
Organizations that have mapped out their funnel and are using mechanisms to track their lifecycle stages are able to understand the velocity at which leads are progressing through the funnel and the rate of conversion from stage to stage.
Having all of this in place empowers leaders with baseline data to understand if what they are doing is making a difference. If the revenue operations team automates two processes within the sales cycle, how much faster is the funnel progressing? If marketing decides to target a specific audience to increase conversion, how many more conversions are actually happening?
What is the best practice for implementing lifecycle stage tracking and what do the three phases look like to get started? Founder & CEO of SaaScend, Craig Jordan, explained them over a Fireside Chat, so that teams could be equipped with the expertise for success.
Phase One: Define Your Lifecycle Stages
Starting from the top of the funnel from when someone first interacts with your business, typically with a marketing campaign, from all the way to when they become a customer, each major stage of transition needs to be defined.
Each organization’s funnel map may look a little different depending on the business, but these are the five recommended to start with.

Standard Stages
#1 Prospect
Anyone that has been identified and entered your marketing automation (MA) system.
#2 Marketing Qualified Lead “MQL”
A lead that has reached the demographic, firmographic, and engagement criteria threshold established by sales and marketing.
#3 Sales Accepted Lead “SAL”
A lead that sales has determined as an acceptable lead to reach out to for further qualification.
#4 Sales Qualified Lead “SQL”
When sales opens an opportunity for the lead and they have entered the pipeline.
#5 Customer
When the buyer becomes Closed Won and has signed the contract.
Once your lifecycle stages have been defined, the recommended method for implementing these into your CRM is via a custom object. This Object is then connected to the Lead, Contact, Opportunity, Account, and Event objects to properly track lifecycle progression through the entire funnel. This allows for reporting on the entire funnel, overcoming separate data tables between Leads and Contacts. The Custom Object solution makes it so teams do not have to try to use third party Business Intelligence tools to visualize it.
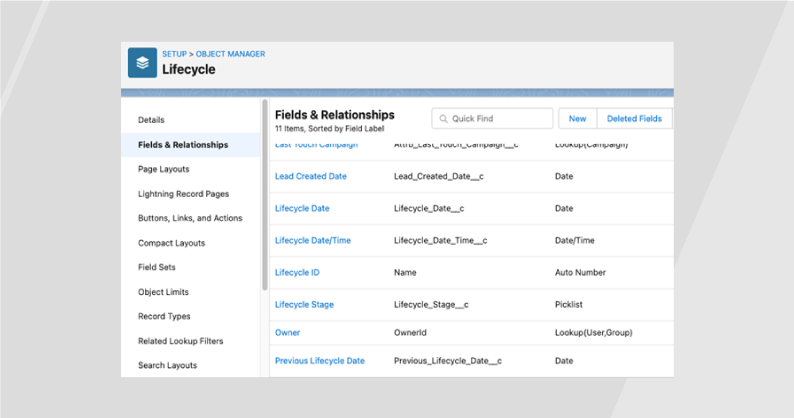
Fig. 1 Lifecycle Custom Object in Salesforce, Fields & Relationships
In addition, on the Lead and Contact objects there needs to be a Lifecycle Stage field (Fig. 1) to denote at a record level the current stage a record is in the funnel. This will help with other systems like a marketing automation platform to market to buyers at a specific stage in the funnel.
Phase Two: Time Stamping
Once the Lifecycle Stage field and custom object are in place, sister date fields for EACH lifecycle stage need to be added to track respective dates of when a lead hits this respective stage. This will be the baseline to track velocity throughout the funnel.
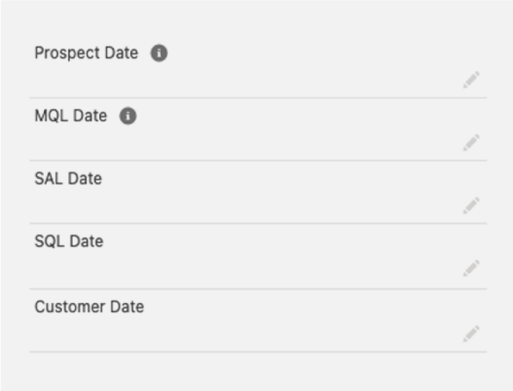
The date fields for each Lifecycle Stage need to be created on the Lead Object and then mapped to the Contact Object, for example, Lifecycle Stage – Lead Date. Automation then needs to be configured to timestamp the update of the Lifecycle Stage field, automatically recording when a lead advances to the next stage on the date field.
The below rule criteria is an example of what can be used to mark the time of a lead being moved to the Customer stage.
AND(
ISPICKVAL (Lifecycle_Stage_c, “Customer”),
Lifecycle_Customer_Date_c=TODAY()
)
As Flows are created for each Lifecycle Stage, teams will then be able to track the velocity of the funnel as leads progress from one stage to the next.

Phase Three: Automation
Automation should be leveraged throughout the funnel, but vital areas are during transition stages as the lead moves from one to the next. What does the hand-off look like from department to department?
Automation should be leveraged throughout the funnel, but vital areas are during transition stages as the lead moves from one to the next. What does the hand-off look like from department to department?
-
-
- What is the process for qualifying a lead?
- How are leads then sent over to sales?
- How does sales follow up?
- What happens if sales follows up and a lead says reach back out in six months?
-
These are all key points throughout the funnel where if automation is not being used to help streamline the process, funnel progression will be slowed.
Lead Qualification
Use a combination of your marketing automation system and your CRM to measure prospect engagement activity and their buyer profile against your MQL criteria.
If your marketing automation does not have a native functionality to give a separate rating for demographic and firmographic data from engagement activity, the CRM automation can be leveraged to award a certain grade level to leads based on their lead record data gathered via the marketing automation form and third-party data enrichment.

Increase Win Rates with Higher
Quality Leads
Marketing to Sales Lead Hand off
Establish a process for your handraise leads and your nurture leads. Handraise leads have taken an action signaling that they are ready to talk to sales. For example at SaaScend, a handraise lead is someone that has submitted to our marketing automation and CRM audit request form, where a nurture lead is someone who may have just downloaded our eBook on attribution.
Sales follow up for handraise leads needs to be as fast as possible. This is where an automated lead routing process can make a huge difference in terms of lead response times and conversion.
Nurture leads should also be passed over to sales with automation, but these are the leads that have interacted with your content and campaigns enough to reach the MQL threshold. These are leads that sales can run outbound campaigns to, to then take further action with those that engage, with the goal of progressing them further down the funnel.
Nurture Campaigns
How many leads say, “Reach out in six months.” and then end up falling through the cracks? To keep this from happening, marketing can set up a nurture campaign that sales can enter their lead into, so that your brand stays top of mind to the prospect. Doing a mix of hard and soft Calls to Action are recommended, to see if marketing can activate any of the leads in the campaign and get them sent back over to sales, progressing them through the funnel.Once your team has defined your lifecycle stages, added the lifecycle stage custom object, created the fields to track time stamps, and have created automations for key funnel transitions, you have started your journey to lifecycle stage tracking optimization.

Gain Funnel Visibility and Increase Your Lifecycle Velocity



